What Is A Smart Card?
A smart card is identical to a credit card in appearance, but inside it is completely different. A credit card is a simple piece of plastic but a smart card contains a microprocessor embedded inside it . The microprocessor is under a gold contact pad on one side of the card. The microprocessor pretty much replaces the usual magnetic stripe on a credit card or bank card.
Magnetic stripe technology widely used still. The data on the stripe can be easily read, written, deleted or changed with equipment you can buy off the shelf. So the stripe is really not the best place to store private/ personal information. To protect us the consumer, businesses have invested in extensive online mainframe-based computer networks for verification and processing.
The microprocessor embedded on the smart card is there for security purposes . The host computer and card reader actually communicate with the microprocessor. The microprocessor enforces access to the data on the card.
Smarts cards may have up to 8 kilobytes of RAM, 346 kilobytes of ROM, 256 kilobytes of programmable ROM, and a 16-bit microprocessor. The smart card uses a serial interface and receives its power from external sources like a card reader. The processor uses a limited instruction set for applications such as cryptography.
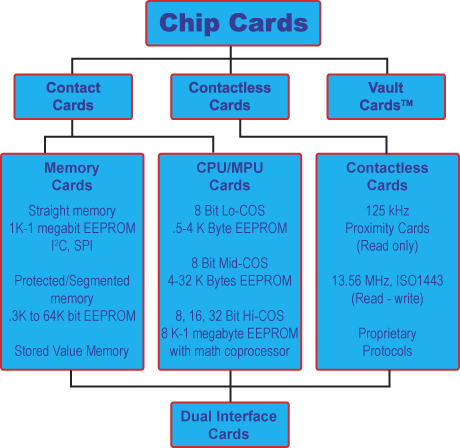 |
Types Of Smart Cards There are 5 main types of cards oout ther. they are:
Contact Cards
Memory Cards
CPU/MPU Microprocessor Multifunction Cards
Contactless Cards
Combination Cards |
Contact Cards
contact cards are the most common type of smart card out there. How it works is that electrical contacts located on the outside of the card connect to a card reader when the card is inserted.
Memory Cards
All memory cards communicate to readers through synchronous protocols. In all memory cards you read and write to a specified address on the card. There are three primary types of memory cards:
1. Straight Memory Cards
These cards just store data and have no data processing capabilities. These cards cannot identify themselves to the reader, so your host system has to know what type of card is being inserted into a reader. These cards are easily duplicated and cannot be tracked by on-card identifiers.
2. Protected / Segmented Memory Cards
These cards have built-in logic to control the access to the memory of the card. Sometimes referred to as Intelligent Memory cards, these devices can be set to write protect some or all of the memory array. Some of these cards can be configured to restrict access to both reading and writing. This is usually done through a password or system key. These cards are not easily duplicated but can possibly be impersonated by hackers. They typically can be tracked by an on-card identifier.
3. Stored Value Memory Cards
These cards are designed for the specific purpose of storing value or for tokens. The cards are either disposable or rechargeable. Most cards of this type incorporate permanent security measures at the point of manufacture. The memory on these devices are set-up as counters. For simple applications such as a telephone card the chip has 60 or 12 memory cells, one for each telephone unit. A memory cell is cleared each time a telephone unit is used. Once all the memory units are used, the card becomes useless and is thrown away. This process can be reversed in the case of rechargeable cards.
CPU/MPU Microprocessor Multifunction Cards
These cards have on-card dynamic data processing capabilities. Multifunction smart cards allocate card memory into independent sections or files assigned to a specific function or application. Multifunction cards benefit issuers by enabling them to market their products and services via state-of-the-art transaction and encryption technology. For the card user, multifunction means greater convenience and security, and ultimately, consolidation of multiple cards down to a select few that serve many purposes.
Contactless Cards
These are smart cards that employ a radio frequency (RFID) between card and reader without physical insertion of the card. Instead the card is passed along the exterior of the reader and read. Types include proximity cards which are made as a read-only technology for building access. These cards function with a limited memory and communicate at 125 MHz.
Combination Cards
These are hybrids that employ both contact and contactless technology in one card. Combi-cards can also contain two different types of chips in contrast to a Dual-Interface card where a single chip manages both functions.
|